Inflammation: The Immune System's Response to Injury + Infection
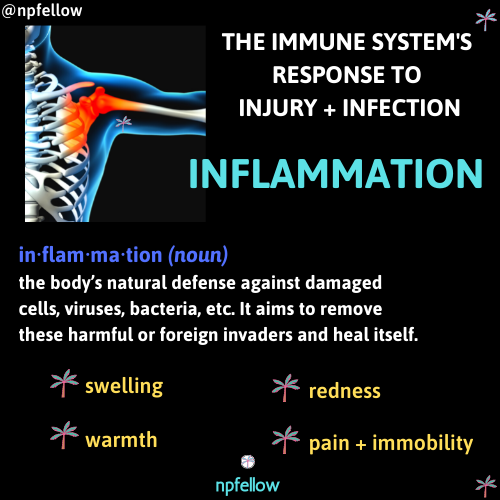
Inflammation is the body’s natural defense against damaged cells, viruses, bacteria, parasites, etc. It aims to remove these harmful or foreign invaders and heal itself. It is the body’s response to infection and a protective process which is beneficial to the body. Cellular injury causes the body to release white blood cells into the blood stream to guard our body from foreign substances, which increases blood flow to the area of injury or infection leading to visible redness, warmth, swelling and pain.
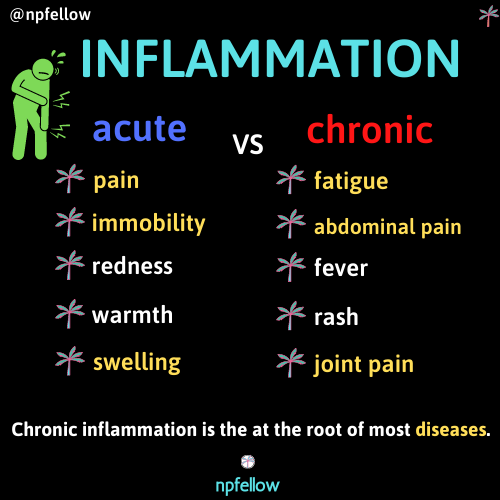
There are two types of inflammation- acute and chronic. Acute inflammation starts quickly and generally disappears in a few days. Chronic inflammation is a result of failure to eliminate the cause that can last from months to years. Acute inflammation is a local response to cellular injury that is marked by capillary dilation, leukocytic infiltration, redness, heat, and pain; and that serves as a mechanism initiating the elimination of noxious agents and damaged tissue. Inflammation is key aspect of the immune system’s response to injury and infection. Acute inflammation helps to heal damaged tissue and defend itself against pathogens like viruses and bacteria. Problems arise when the inflammatory process goes on for too long and becomes chronic. Chronic inflammation is the at the root of most diseases.
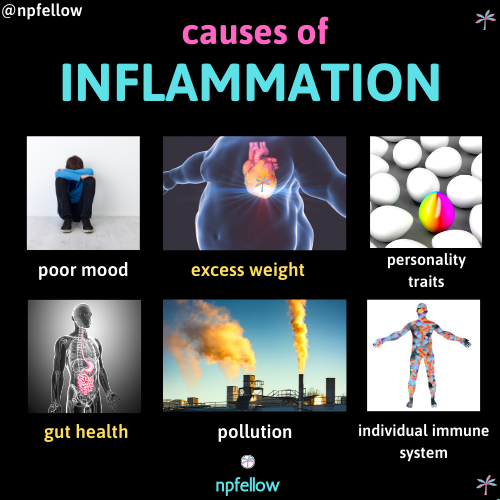
There are multiple causes for inflammation. The inflammatory process is individualized for each person. Some bodies don’t handle infection well with a normal acute or temporary inflammatory response. A malfunctioning protein- CYLD a.k.a., the immune system’s break pedal is crucial for managing the body’s inflammatory response to pathogens like bacteria and viruses. When this protein malfunctions or has a defect it can cause the inflammatory response to go out of control. Excess weight or obesity can cause inflammation through the entire body. Extra fatty tissue produces cytokines (proteins secreted by the immune system) in the body, which puts the body in a long-term, low grade inflammatory state. Poor m00d and depression is linked to increased levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), which is a protein part of the inflammation response. So when our mood is down CRP is increases; thus, increasing inflammation. Certain personality traits can cause inflammation. People who are less conscientious are more likely to have unhealthy habits that promote inflammation like smoking, eating unhealthy food and exercising less. Poor gut health and gut dysbiosis- when are gut bacteria is imbalanced, can result in inflammation both inside the bowel and outside the digestive system. Environmental toxins and pollution exposure is linked to higher levels of CRP and cytokines; thus, increasing inflammation.
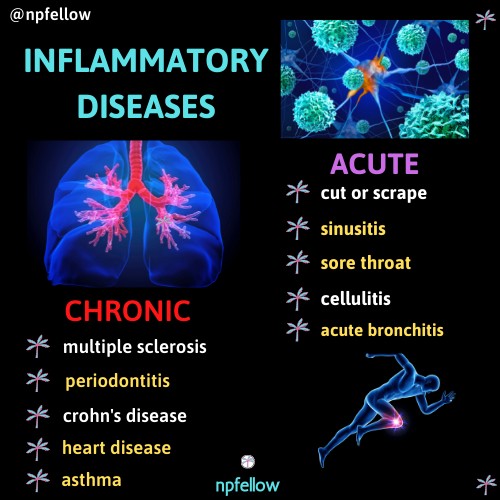
Inflammation can be self-limiting for a short period of time or it can become chronic and cause disease. Chronic inflammation is at the root of almost all disease. Excess weight puts the body is a long-term, low grade state of inflammation. These are some acute vs chronic inflammatory conditions.
Acute conditions include, but are not limited to sore throat due to a cold or flu, skin wound like a cut or scrape, infected ingrown hair, physical trauma, acute bronchitis, sinusitis, and cellulitis. Chronic inflammatory diseases include, but are not limited to asthma, heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, peptic ulcer disease, periodontitis, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease.

Natural remedies for inflammation include anti-inflammatory foods, red wine and quercetin-rich foods, anti-inflammatory supplements, and anti-inflammatory practices. Anti-inflammatory foods are also rich in antioxidants, which reduce the damage caused by inflammation. Eating a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods places our body in a state conducive to healing from diseases. Anti-inflammatory foods include broccoli, collard greens, kale, Cabbage, cauliflower, spinach, Mixed, berries, pineapple, oranges, Celery, cucumber, lemon, Pineapple, pomegranate,, grapefruit, Water, unsweetened herbal teas, Beans, chickpeas, lentils, Garlic, ginger, turmeric, thyme, Cinnamon, chili peppers, rosemary, Organic eggs, grass-fed meat. Red wine is full of quercetin, which is a very important flavonoid and is packed with potent anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, and anti-carcinogenic properties. Quercetin is able to modify inflammation and inhibit inflammatory enzymes, and can also be found in green tea. Anti-inflammatory supplements include omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, willow bark, and bromelain (found in pineapple).
Daily anti-inflammatory practices are the key for being in a low grade anti-inflammatory state. Moderate exercise for 20 minutes reduces inflammatory responses and protects against chronic conditions. Prayer and meditation also helps to decrease inflammation by reducing stress and deactivating the activity of genes associated to inflammation.
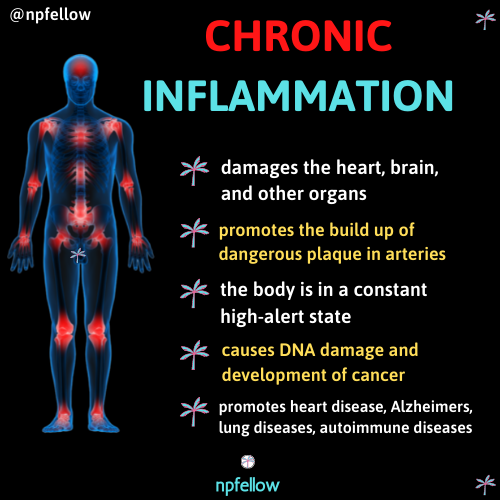
It is important to understand the detrimental effects of chronic inflammation and why it is so crucial that we decrease/eliminate it. When the body is in a long term state of low grade inflammation, it is constantly in a state of high alert, which puts the body in panic mode. Chronic inflammation damages the heart, the brain and other organs. Inflammation in the arteries stimulates dangerous plaque formation. A vicious cycle of plaque formation and the clotting cascade further clogs arteries creating a blockage of blood flow- leading to strokes and heart attacks. Chronic inflammation promotes heart disease, lung disease, Alzheimer’s disease and autoimmune disorders. It is at the root of almost all disease. Inflammation causes DNA damage and leads to the development of cancer. It is the perfect environment for cancer to thrive in.
Final Thoughts
Inflammation is the body’s natural defense against damaged cells, viruses, bacteria, etc. It aims to remove these harmful or foreign invaders and heal itself. It is the body’s response to infection and a protective process which is beneficial to the body. Cellular injury causes the body to release white blood cells into the blood stream to guard our body from foreign substances, which increases blood flow to the area of injury or infection leading to visible redness, warmth, swelling and pain. There are two types of inflammation- acute and chronic. Acute inflammation starts quickly and generally disappears in a few days. Chronic inflammation is a result of failure to eliminate the cause that can last from months to years.
acute inflammation is a local response to cellular injury that is marked by capillary dilation, leukocytic infiltration, redness, heat, and pain; and that serves as a mechanism initiating the elimination of noxious agents and damaged tissue. Inflammation is key aspect of the immune system’s response to injury and infection. Acute inflammation helps to heal damaged tissue and defend itself against pathogens like viruses and bacteria. Problems arise when the inflammatory process goes on for too long and becomes chronic. Chronic inflammation is at the root of most diseases.
Thank you for reading this post.
